Diabetes Management And A1C Levels
Introduction
Effective diabetes management is crucial for leading a healthy life with diabetes. A key indicator of how well diabetes is controlled is the A1C levels, which reflect average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Understanding the relationship between A1C levels and blood sugar control can empower individuals with diabetes to make informed health and treatment decisions.
1. Understanding A1C Levels
What is A1C?
The A1C test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood that is coated with sugar (glycated). This test provides an overview of your average blood glucose levels over the previous 2-3 months, making it a vital tool in diabetes management.
Normal and Dangerous Levels of A1C
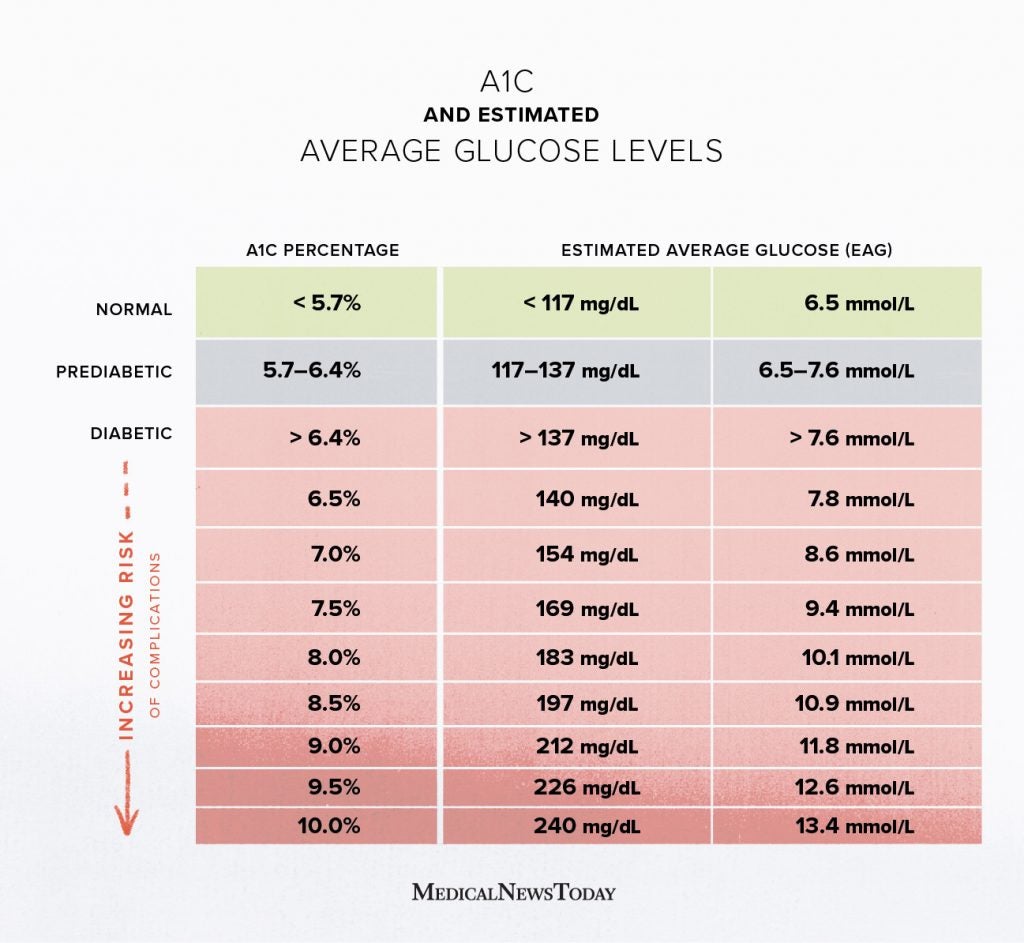
- Normal A1C Levels: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Consult an A1C chart to quickly assess your status. Levels above 7% may indicate poor blood sugar control.
Understanding A1C Results
Interpreting your A1C results is essential. A higher A1C level suggests that blood sugar levels have been higher than the target range, which can lead to complications if not addressed.
2. A1C and Diabetes
A1C Levels and Diabetes
A1C levels are pivotal in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. They help healthcare providers understand how well blood sugar levels have been managed over time.
A1C Goals for Patients
Recommended A1C goals can differ based on individual circumstances, but generally:
- For most adults with diabetes: Below 7%
- For some older adults or those with comorbid conditions: Above 7%
High A1C Symptoms
Elevated A1C levels can lead to symptoms such as:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Long-term Effects of High A1C Levels
Prolonged high A1C levels can cause severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision issues. Regular monitoring is vital for prevention.
3. Managing A1C Levels
How to Lower A1C Levels
Here are strategies to effectively lower your A1C levels:
- Medication adherence: Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations.
- Regular monitoring: Frequently monitor your blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle changes: Incorporate healthy habits.
A1C and Diet
Diet plays a significant role in diabetes management. Focus on:
- Whole grains and fiber-rich foods
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- Limiting sugars and processed foods
Impact of Exercise on A1C
Regular physical activity can significantly improve blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can enhance insulin sensitivity.
Factors Affecting A1C Levels
Several factors can influence your A1C results, including:
- Stress
- Illness
- Medications (some can raise blood sugar levels)
4. Testing and Monitoring A1C Levels
A1C Testing Frequency
For individuals with diabetes, it's recommended to have A1C levels checked at least twice a year if you meet your targets, and quarterly if your treatment has changed or you're not achieving your goals.
A1C Monitoring Devices
Various devices are available for monitoring A1C levels, such as:
- Point-of-care testing devices: Provide quick results but may not be as accurate as lab tests.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): Help track blood sugar in real-time but may not provide A1C results directly.
A1C vs. Blood Glucose
While A1C testing gives an overview of average blood sugar levels, daily blood glucose monitoring allows for immediate insights into your current blood sugar levels. Both are vital for comprehensive diabetes management.

Conclusion
Understanding and managing your A1C levels is fundamental for effective diabetes management. By incorporating healthy dietary choices, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring, individuals with diabetes can achieve better health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.